
They almost must have a minimum of 8 years of time in service. With the new system, Staff Sergeants now have a minimum Time in Grade (TIG) requirement, as well as a Time in Service (TIS) requirement.ĭepending on their MOS, E-6 sergeants must spend from 36 to 48 months in grade before being considered for promotion to E-7, Sergeant First Class. The Army changed how it promotes Senior NCOs recently. Master Sergeant and First Sergeant share the grade of E-8, but they have different roles and responsibilities in the Army. There are only three pay grades in this set of ranks. Senior noncommissioned officers have a higher level of responsibility. Completion of the Primary Leadership Development CourseĪ Staff Sergeant works closely with other sergeants on the development of soldiers in their section.Ĭandidates for Staff Sergeant must be meet the following requirements to be eligible for promotion:Īrmy Promotion Timeline for Senior NCO Image: army.mil.To make Corporal, Specialists must complete Basic Leader Course (BLC) and be recommended for advancement by a promotion board.Ĭorporals hoping for a promotion to E-5 must meet the following expectations: Specialist E-4s must first be promoted to Corporal E-4 before becoming eligible for the rank of Sergeant. Sergeant (E-5)Īdvancement to a Sergeant is competitive in the Army. You also need a security clearance that matches your MOS. Your unit commander can promote you to Corporal if you have 26 months in service, along with six months of time in grade (three with a waiver). However, a Corporal, despite being the lowest rank possible for a noncommissioned officer, is more about leadership. However, even though these two have the same pay rank, they have different responsibilities.Ī Specialist is known for having technical experience and knowledge. The lowest noncommissioned officer rank is a Corporal.Īlso, you might notice that the E-4 designation for the Corporal is the same as the Specialist in the Junior Enlisted ranks. There are three levels of Noncommissioned officers in the Army. Related Article – What Happens After Army Boot Camp? Army Promotion Timeline for NCO Ranks Image: Lastly, to continue to a Specialist (E-4), you will need two years of service and at least six months of time in pay grade. E-1 is the initial rank for those just coming out of basic training.Īlso, to promote to an E-2, which is a private second-class (PV2), you need six months of service or four months of service with advanced college or ROTC.Īfterward, promotion to an E-3, or private first class (PFC), happens after 12 months of enlistment and at least four months as an E-2.

Army Promotion Timeline for Junior Enlisted Ranks Image: Īn E-1 is the lowest rank in the Army.
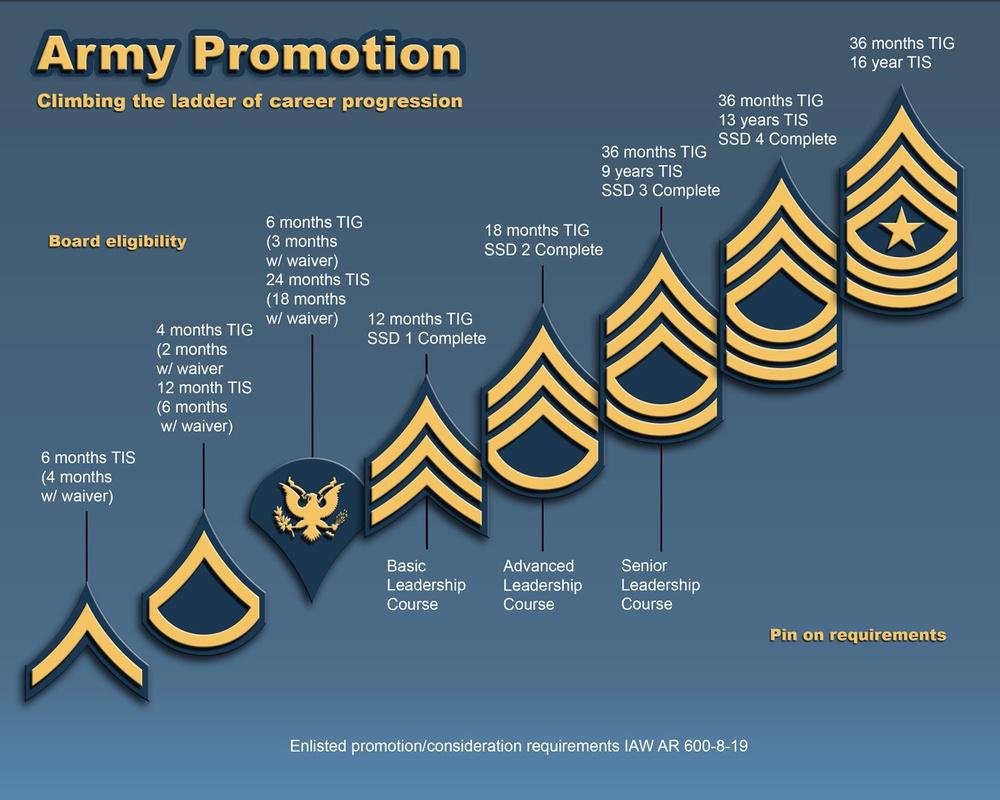
However, the higher up the promotion rank, the more competitive promotions become. The Army bases some of its promotion criteria on time in service and time in pay grade.


These ranks break into Junior enlisted, Noncommissioned officers, and Senior Noncommissioned officers.Īlso, the Army has commissioned officers. The Army consists of 13 different enlisted ranks. When considering your career in the Army, it is vital to consider the Army promotion timeline when you plan.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
